Proximity sensors are integral components in a wide range of modern applications, from smartphones and automobiles to industrial automation and robotics. They enable devices to detect the presence of nearby objects without physical contact, offering a versatile and efficient means of control, safety, and automation. This guide aims to provide prospective buyers with a comprehensive understanding of proximity sensors, covering their functionality, various types, applications, selection criteria, and frequently asked questions.
How Proximity Sensors Work:
At their core, proximity sensors function by emitting a field of energy (electromagnetic or acoustic) and detecting changes in that field caused by the presence of a target object. The sensor then converts this change into an electrical signal, which can be used to trigger an action, such as activating an alarm, stopping a machine, or counting objects. Crucially, this detection occurs without the sensor physically touching the target, minimizing wear and tear and enabling detection of fragile or sensitive objects.
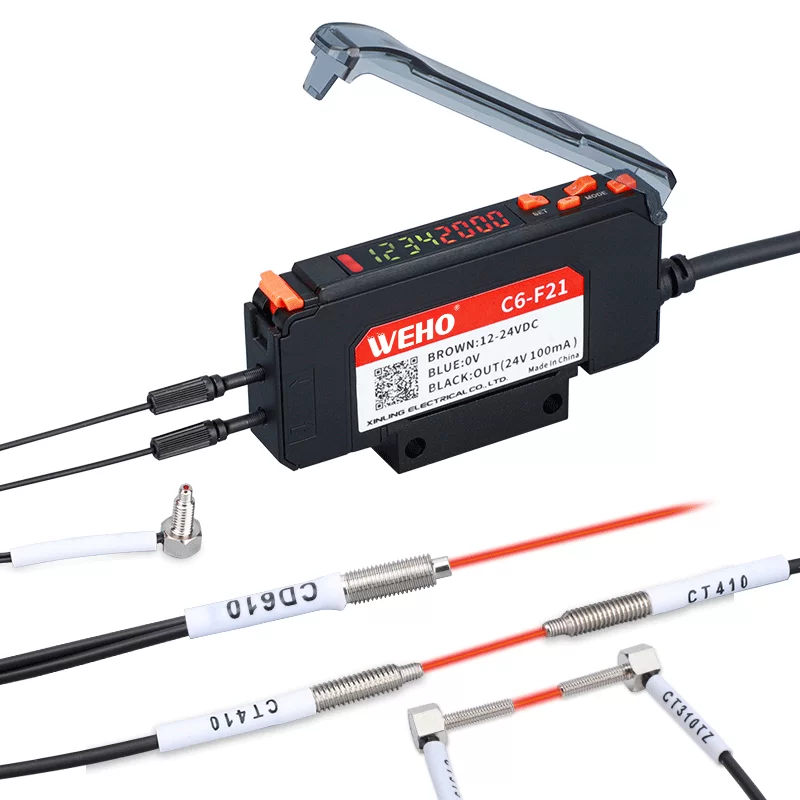

Types of Proximity Sensors:
Setallic objects. They are robust, reliable, and widely used in industrial automation for applications like position sensing, counting metal parts, and limit switching.everal different types of proximity sensors cater to specific needs and operating environments. Understanding the distinctions is crucial for selecting the appropriate sensor for your application. The most common types include:
- Inductive Proximity Sensors: These sensors use a magnetic field to detect metallic objects. They are robust, reliable, and widely used in industrial automation for applications like position sensing, counting metal parts, and limit switching.
- Capacitive Proximity Sensors:These sensors utilize an electric field to detect both metallic and non-metallic objects, including liquids, powders, and plastics. Their versatility makes them suitable for applications such as level detection, material handling, and presence sensing.
- Photoelectric Sensors:These sensors employ a beam of light (typically infrared) to detect the presence or absence of an object. They offer long sensing ranges and are commonly used in applications such as object detection, conveyor belt monitoring, and safety systems.
- Ultrasonic Proximity Sensors:These sensors emit ultrasonic waves and measure the time it takes for the reflected waves to return to the sensor. This allows them to detect objects regardless of their material or color, making them suitable for applications in challenging environments such as dusty or dirty areas.
- Magnetic Proximity Sensors (Reed Switches):These sensors utilize a magnetic field to activate a switch. They are simple, cost-effective, and commonly used in security systems, door and window sensors, and position sensing.
Key Considerations for Selecting a Proximity Sensor:
Choosing the right proximity sensor requires careful consideration of several factors:
Sensing Range: The maximum distance at which the sensor can reliably detect an object.
Target Material: The material of the object being detected.
Operating Environment: Factors such as temperature, humidity, and the presence of dust or liquids.
Output Type: The type of electrical signal produced by the sensor (e.g., digital, analog).
Mounting Style: How the sensor will be physically attached to the system.
Response Time: The time it takes for the sensor to react to the presence or absence of an object.
Cost: Balancing performance requirements with budget constraints.
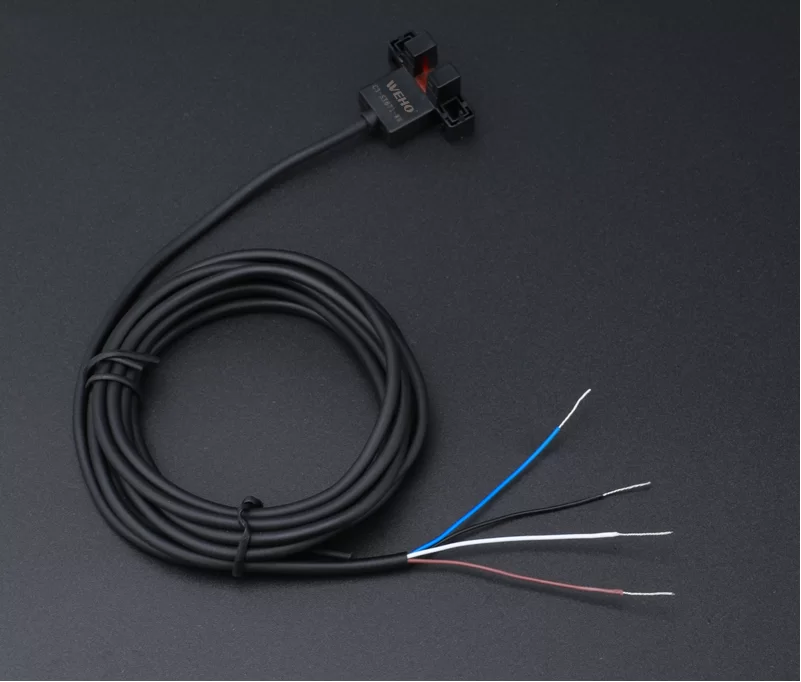

Applications of Proximity Sensors:
The applications of proximity sensors are vast and continually expanding. Some prominent examples include:
Industrial Automation: Controlling robotic arms, monitoring conveyor belts, counting parts, and ensuring safety.
Automotive: Parking assistance, collision avoidance, seatbelt detection, and airbag deployment.
Consumer Electronics: Smartphone screen activation, touchless faucets, and automatic soap dispensers.
Security Systems: Door and window alarms, intrusion detection, and access control.
Medical Devices: Patient monitoring, respiratory rate detection, and proximity detection for surgical instruments.
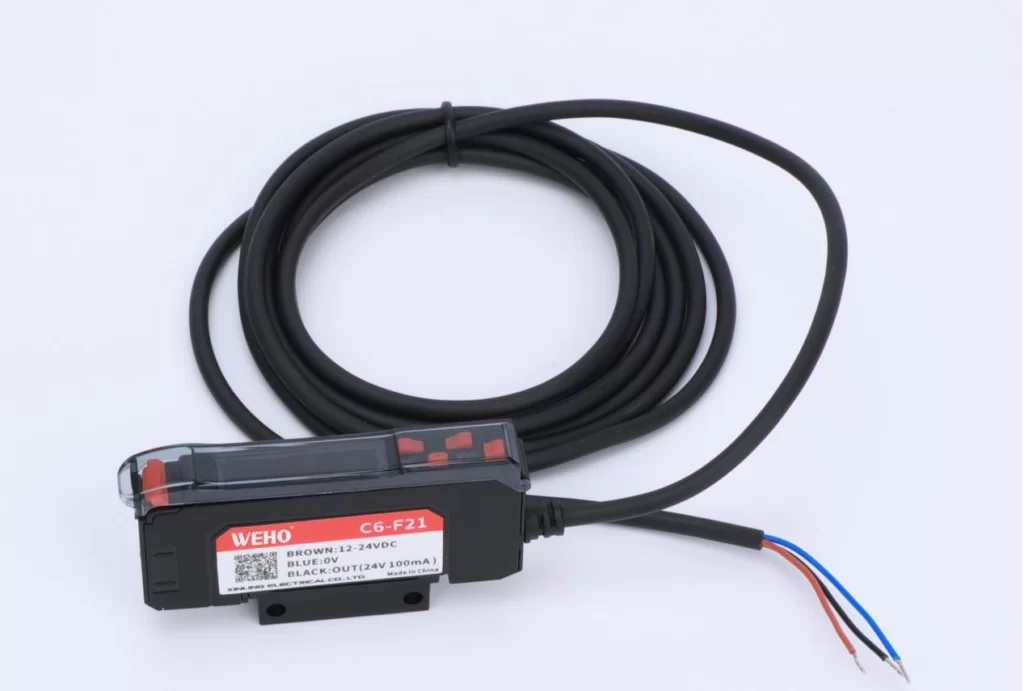

Conclusion:
Proximity sensors are indispensable components in a wide array of applications, providing contactless detection, enhanced safety, and improved automation. By understanding the different types of proximity sensors available and carefully considering your specific application requirements, you can make an informed purchasing decision and leverage the power of this versatile technology. If you have further questions or require assistance in selecting the right sensor for your needs, please don’t hesitate to contact a qualified supplier or manufacturer for expert guidance.If you Interested in Proximity Sensor and have suggestions for my Blog.Please Contact me on https://wehopower.com/ or Whatsapp:+86 18991841394 Thank you for reading this blog.