What is a Temperature Controller?
A temperature controller is an electronic device used for controlling temperature within a pre-defined range by receiving temperature readings to switch the heating or cooling on and off. These devices are common in industries which require accurate range of temperature. In addition, they also feature PID control which helps in foreseeing the temperature thus allowing quick adjustments. For instance, digital temperature controllers offer high degree of precision and adjustment in temperature during the processes involved in manufacturing, food treatment and chemical reaction.
Is a Thermostat Just a Switch?

No, a thermostat is not just a switch. A thermostat is more advanced as it not only functions as a switch but can monitor various heating or cooling equipment. For instance, if the temperature in the room is higher than the set capacity, the device can automatically shut off the heater and vice versa. Termostats range from simple mechanical switches to advanced electronic switches with integrated circuits for enhanced sensitivity and precision.
Can a thermostat control temperature?
Yes, a thermostat can help control temperature, but it depends on how the thermostat is built. Basic models simply turn a heating or cooling unit on or off when a specific temperature is reached. Advanced digital models regulate the temperature within much tighter thresholds.
What is RC vs C on thermostat?
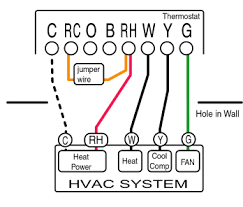
They are wires for the thermostat RC (Rh) and C (Common) can be found on the terminal section of the thermostat.
- RC: This terminal connects to the cooling system of the HVAC unit and serves as the Cool signal.
- C: The common wire terminal usually provides the 24 volt power supply needed to operate the thermostat.
Your thermostat is able to operate both with heating and cooling systems because these terminals help facilitate primary wiring.
What are the 6 Differences Between a Thermostat and a Temperature Controller?
| Category | Thermostat | Temperature Controller |
| Purpose | Controls temperature in homes, offices, and appliances like heaters and ACs. | Maintains precise temperatures in industries, labs, and production processes. |
| Operation | Turns heating/cooling on or off based on temperature changes. | Uses sensors and PID control for continuous temperature adjustments. |
| Applications | Found in HVAC systems, water heaters, and ovens. | Used in incubators, autoclaves, brewing, and industrial machines. |
| Feedback | Works with a simple on/off system. | Uses a closed-loop system for better accuracy. |
| Precision | Provides basic temperature control. | Ensures high accuracy and fast response. |
| Features | Uses mechanical or electronic parts for simple control. | Offers advanced features like PID control, programmability, and remote access. |
Purpose
Thermostat: Aids the temperature maintenance of a dwelling or an office space and appliances such as air conditioners, heaters, and even fridges. The thermostat ensures that a space achieves a temperature that is satisfactory.
Temperature Controller: Designed to maintain regulated temperatures in an industry, laboratory or during production where a specific temperature is needed for chemical reactions, food pasteurization, or equipment tests.
Operation
Thermostat: Works by sensing a change in temperature, and based on it, controls the heating and cooling systems by switching them on and off. Simple mechanical thermostats use bimetallic strips while electronic versions utilize sensors and microcontrollers.
Temperature Controller: Employs specific sensors to gauge temperatures and utilizes advanced control technologies such as PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) to maintain control and continuously adjust setpoint temperatures unlike a thermostat.
Applications
Thermostat: Present in domestic and commercial HVAC equipment, water heaters, and ovens. Found in appliances that require basic temperature control.
Temperature Controller: Found in specialty incubators, autoclaves, brewing systems, and industrial machines that need to be constantly and accurately monitored and adjusted.
Feedback Mechanism
Thermostat: Directly enables or disables heaters and coolers to monitor temperatures and uses a device’s set point as a threshold.
Temperature Controller: This device employs a closed-loop mechanism which enables tight control and helps in preventing undershooting or overshooting of temperature sought after.
Precision
Thermostat: This equipment is set for a moderate amplification and is able to adjust in a range of narrow limits. This makes it efficient for comfort tempering.
Temperature Controller: In an industrial or scientific settings in which precise responses are of the utmost importance, a temperature controller can outperform with its increased mobility alongside high response rate with accuracy.
Weho – TX4 Series PID Temperature Controller
TX4 series economic four-digit dual display PID temperature controller has 100ms high-speed sampling period and ±0.5% display accuracy, can independently switch relay contacts or SSR drive output, and the upper limit configuration has two alarm outputs.
Features
Thermostat: This device encompasses either mechanical or electrical parts which enable it to function, albeit at a rate which can be termed basic. A thermostat can be operated to execute basic temperature moderation, although the extent of the desired moderation remains limited.
Temperature Controller: Offers advanced features such as PID control techniques, programmability, high accuracy, and sometimes, remote access, which leads to enhanced performance in complex temperature regulation tasks These rituals are but a few of the many areas in which temperature controllers succeed over their predecessors.
Is a Temperature Controller Better Than a Thermostat?
The answer to whether a temperature controller is superior to a thermostat has no single answer. For domestic and some business uses, a thermostat is adequate and economical for comfort maintenance purposes. But, for inverters or other businesses needing accurate and constant temperature control, a temperature controller is the best option. It is true that its additional features, such as PID control, guarantee greater temperature control.
Discover the Best Temperature Control Solutions
Conclusion
As with most things, both the thermometer and temperature controller are important in temperature measurement, but they vary in features and accuracy. While thermostats are suited for general use in homes and businesses, temperature controllers are better for areas with high precision requirements. Knowing these differences helps in the selection of the appropriate appliance.
WehoPower – Your Best Pid Temperature Controller Manufacturer
At WehoPower, we are a leading PID temperature controller manufacturer in China. We offer the TX4 Series PID temperature controllers, which include five different models. The primary distinction between these models is the size of the device itself in addition to the size of the hole. Regardless of whether you require a more powerful, larger PID temperature controller or one that is more compact, our inventory will have the right one. Reach out to us today, and discover the best offer on the PID temperature controllers.

References
Thermostat vs Temperature Controller: Key Differences Explained
The Differences Between a Temperature Controller And a Thermostat
Guide to Thermostats vs. Digital Temperature Controllers