What is a Prox Switch?

A proximity switch, often referred to as a prox switch, is a type of sensor that detects the presence or absence of an object without the need for direct contact. These sensors are used in various applications, including automation systems, to detect objects, position, or speed in a range of industries such as manufacturing, robotics, and packaging.
What Are the 2 Main Types of Prox Switch?
There are two primary types of proximity sensors used in industrial applications:
- Inductive Proximity Sensor: Primarily used for detecting metallic objects.
- Capacitive Proximity Sensor: Used for detecting both metallic and non-metallic objects such as liquids, plastics, and paper.
What is an Inductive Sensor?

An inductive sensor works based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. It generates an electromagnetic field and detects changes in this field when a metallic object enters the sensing range. The presence of the metal alters the oscillation amplitude of the sensor, which is then processed by the internal circuitry to trigger an output signal.
What is a Capacitive Sensor?

A capacitive sensor, on the other hand, uses an electrostatic field to detect the presence of an object. The sensor measures the change in capacitance between the sensor and the object. This type of sensor can detect both metallic and non-metallic objects, including liquids, plastics, and more, depending on the material’s ability to affect the electrostatic field.
Inductive vs Capacitive Sensor: 9 Differences
| Feature | Capacitive Sensor | Inductive Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| Circuit and Composition | Contains an electrode and oscillator that creates an electrostatic field. | Contains a coil and oscillator that generates an electromagnetic field. |
| Working Principle | Detects changes in capacitance between the sensor and the object. | Detects changes in electromagnetic oscillations caused by the presence of metal. |
| Detection Objects | Detects both metallic and non-metallic objects, including liquids, plastics, paper, and powders. | Detects only metallic objects. |
| What Sensor Can Detect Paper | Preferred choice for detecting paper and non-metallic objects. | Cannot detect paper. |
| Usage Environment | Suitable for dusty, dirty, or liquid environments; affected by extreme temperatures or chemicals. | Ideal for harsh environments with metals; not affected by dirt or moisture. |
| Detection Distance | Shorter detection range, varies depending on object size and material. | Longer detection range, especially for large metal objects. |
| Accuracy and Sensitivity | Highly sensitive, can detect small objects but prone to false triggering. | Highly accurate for metal objects, less sensitive to non-metallic materials. |
| Anti-interference Ability | More susceptible to interference from humidity, temperature, and electromagnetic fields. | Better anti-interference ability, less affected by environmental changes. |
| Response Speed | Fast response, but sensitivity may cause delays in detection of small objects. | Fast response, reliable in high-speed applications involving metal. |
| Price | Generally more expensive due to versatility in detecting various materials. | Typically less expensive, as they are designed for detecting only metal. |
Circuit and Composition
Capacitive Sensor
Capacitive sensors contain an electrode and an oscillator circuit that creates an electrostatic field. The sensor works by detecting changes in capacitance as objects enter this field.
Inductive Sensor
Inductive sensors, on the other hand, consist of a coil and an oscillator that generates an electromagnetic field. They detect metallic objects by measuring changes in the oscillation amplitude caused by the presence of the metal.
Working Principle
Capacitive Sensor
Capacitive sensors detect objects based on the changes in capacitance between the sensor and the object. When the capacitance alters due to an object entering the electrostatic field, it causes the sensor’s internal circuitry to oscillate, which triggers the sensor’s output.
Inductive Sensor
Inductive sensors detect objects through electromagnetic induction. The presence of a metallic object dampens the sensor’s electromagnetic oscillations, which is detected by the sensor to trigger an output signal.
Detection Objects
Capacitive Sensor
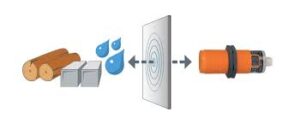
Capacitive sensors can detect both metallic and non-metallic objects, including liquids, plastics, paper, and even powders.
Inductive Sensor
Inductive sensors are only capable of detecting metallic objects. They cannot detect non-metallic materials such as plastic, paper, or liquids.
What Sensor Can Detect Paper
A capacitive sensor is the preferred choice for detecting paper as it can sense non-metallic objects like paper and plastic.
Usage Environment
Capacitive Sensor
Capacitive sensors are versatile and can be used in environments with dust, dirt, or liquids. However, their performance can be affected by extreme temperatures or chemicals that might alter the material’s capacitance.
Inductive Sensor
Inductive sensors are ideal for harsh environments where metals are present, as they are durable and not affected by dirt or moisture. However, they are limited to detecting only metal objects.
Detection Distance
Capacitive Sensor
The detection range of capacitive sensors can vary depending on the material and size of the object being detected. Generally, their detection distance is shorter compared to inductive sensors.
Inductive Sensor
Inductive sensors typically have a longer detection distance compared to capacitive sensors, especially when detecting large metal objects.
Accuracy and Sensitivity
Capacitive Sensor
Capacitive sensors tend to be more sensitive and can detect smaller objects or even slight changes in material properties. However, this high sensitivity may also make them more prone to false triggering.
Inductive Sensor
Inductive sensors are less sensitive to non-metallic objects but are highly accurate when detecting metal objects. They are less prone to interference and provide reliable measurements in metal-dominated environments.
Anti-interference Ability
Capacitive Sensor
Capacitive sensors are more susceptible to interference from external factors such as humidity, temperature, and electromagnetic fields. These factors can lead to false readings if not properly shielded.
Inductive Sensor
Inductive sensors generally have better anti-interference abilities, particularly in environments with high electrical noise or dust. Their electromagnetic field is less affected by environmental changes compared to capacitive sensors.
Response Speed
Capacitive Sensor
Capacitive sensors offer fast response times, making them suitable for high-speed applications, although their sensitivity to small objects can sometimes delay detection.
Inductive Sensor
Inductive sensors also provide fast response times, and their performance is typically very reliable in high-speed applications involving metal detection.
Price
Capacitive Sensor
Capacitive sensors are generally more expensive due to their versatility in detecting a wide range of materials, including both metallic and non-metallic objects.
Inductive Sensor
Inductive sensors are typically less expensive than capacitive sensors since they are designed specifically for detecting metal objects.
Find the Best Inductive Sensor at WehoPower
If you are looking for high-quality inductive sensors, WehoPower‘s Inductive Sensor is a high-performance sensor widely used in industrial automation, particularly for precise metal object detection in various applications. Its simple design and easy installation, combined with multiple protective features, ensure stable operation even in harsh environments.
Key Features of WehoPower Inductive Sensor
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Simple Wiring, Easy Installation | Quick and easy installation with minimal wiring required, saving time and costs. |
| Multiple Protection Features | Polarity and overcurrent protection to prevent damage and ensure durability. |
| Dual Light Indicators | Green power and red action indicator lights for real-time status updates. |
| IP67 Protective Structure | Dust and water resistant, suitable for harsh environments. |
| Wide Operating Temperature | Efficient in temperatures ranging from -25°C to +70°C. |
| Excellent Oil Resistance | Highly resistant to oils, ideal for mechanical and manufacturing environments. |
Conclusion
Inductive and capacitive proximity sensors each have their unique strengths, making them ideal for different applications. While inductive sensors are better suited for detecting metal objects in harsh environments, capacitive sensors offer greater versatility by detecting both metallic and non-metallic objects.
When choosing between the two, consider factors like detection distance, sensitivity, and the type of materials involved in your application. To find the right sensor for your needs, check out WehoPower’s selection of inductive sensors and more.
References
Capacitive vs Inductive Proximity Sensor: 5 Things to Know