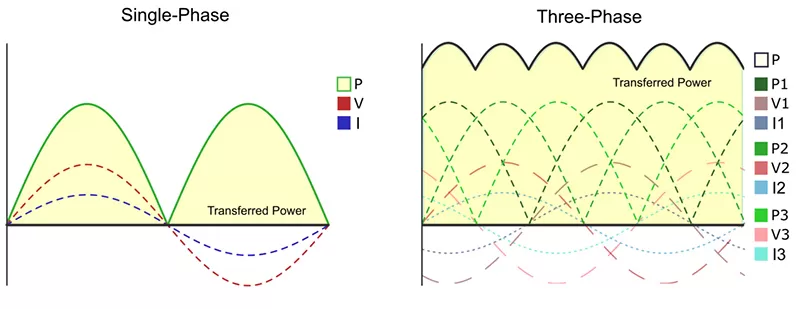
Electricity is the foundational element for any electronic apparatus, and its provision originates from a power source.
The manifestation of electricity can be seen in two distinctive forms: Alternating Current (AC) or Direct Current (DC).
The primary distinction between AC and DC lies in the movement pattern of electrons.
In Direct Current, electrons maintain an unwavering course, flowing consistently in one direction, conversely, Alternating Current experiences a frequent alteration in electron flow direction — progressing forwards before retreating backwards routinely.
Two powerful forces, alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC), each defend their territory. These currents fuel our homes and power our vehicles. In this article, let’s explore what makes this current different.