In the realm of switched-mode power supplies (SMPS), the terms “power supply” and “transformer” are often used, sometimes interchangeably. This can lead to confusion, especially for those new to the field. While a transformer is a crucial component within many power supplies, it’s essential to understand that they are not synonymous. A power supply is a complete system, while a transformer is a specific component within that system. Let’s delve deeper to clarify the distinctions and explore their intricate relationship within SMPS designs.
Understanding the Power Supply
A power supply unit (PSU), at its core, is an electronic circuit designed to convert electrical power from one form to another, typically from AC line voltage to a regulated DC voltage suitable for powering electronic devices. This conversion isn’t a single-step process; it involves a series of transformations:
Rectification: Converting the AC input to pulsating DC.
Filtering: Smoothing out the pulsating DC to a more stable DC level.
Voltage Regulation: Maintaining a constant output voltage despite variations in input voltage or load current.
Isolation (often): Separating the input and output circuits for safety and noise reduction.
Protection: Implementing safeguards against overcurrent, overvoltage, and short circuits.
A complete power supply, therefore, encompasses a multitude of components, including rectifiers, filters, switching elements (like MOSFETs), control circuitry, and often, a transformer. It’s the entire system responsible for delivering stable, reliable power.
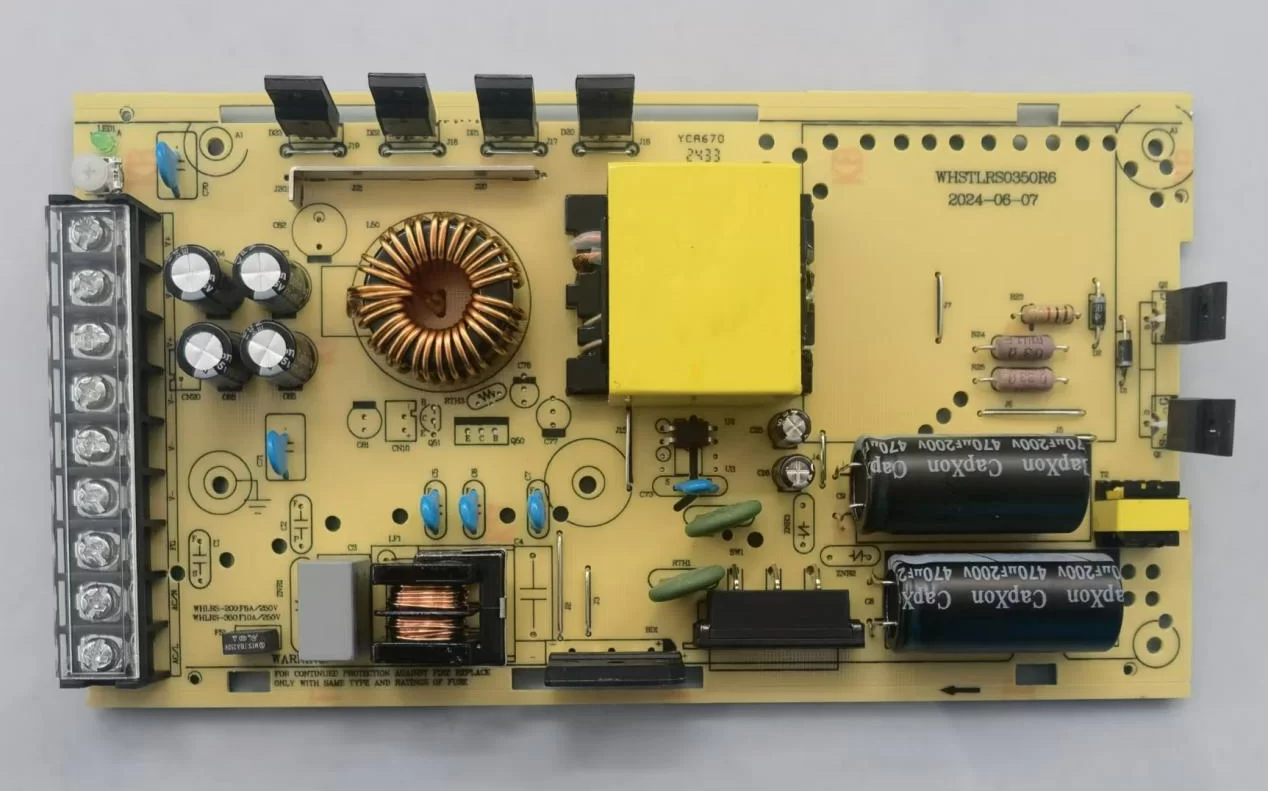
The Role of the Transformer
A transformer, on the other hand, is a passive electrical component that transfers electrical energy between two or more circuits through inductive coupling. It consists of two or more coils of wire (windings) wound around a common ferromagnetic core. When an alternating current flows through the primary winding, it creates a magnetic flux in the core. This flux, in turn, induces a voltage in the secondary winding.
The key functions of a transformer within a power supply are:
Voltage Transformation: Stepping up or stepping down the voltage level. This is crucial for matching the AC line voltage to the desired DC output voltage.
Isolation: Providing electrical isolation between the input and output circuits. This is vital for safety, preventing dangerous voltages from reaching the load and minimizing noise coupling.
Impedance Matching: Optimizing the transfer of power between different parts of the circuit.
In SMPS specifically, transformers operate at high frequencies (tens to hundreds of kilohertz), allowing for smaller and lighter components compared to traditional line-frequency transformers. They play a pivotal role in the switching process, energy storage, and voltage conversion within the SMPS topology.
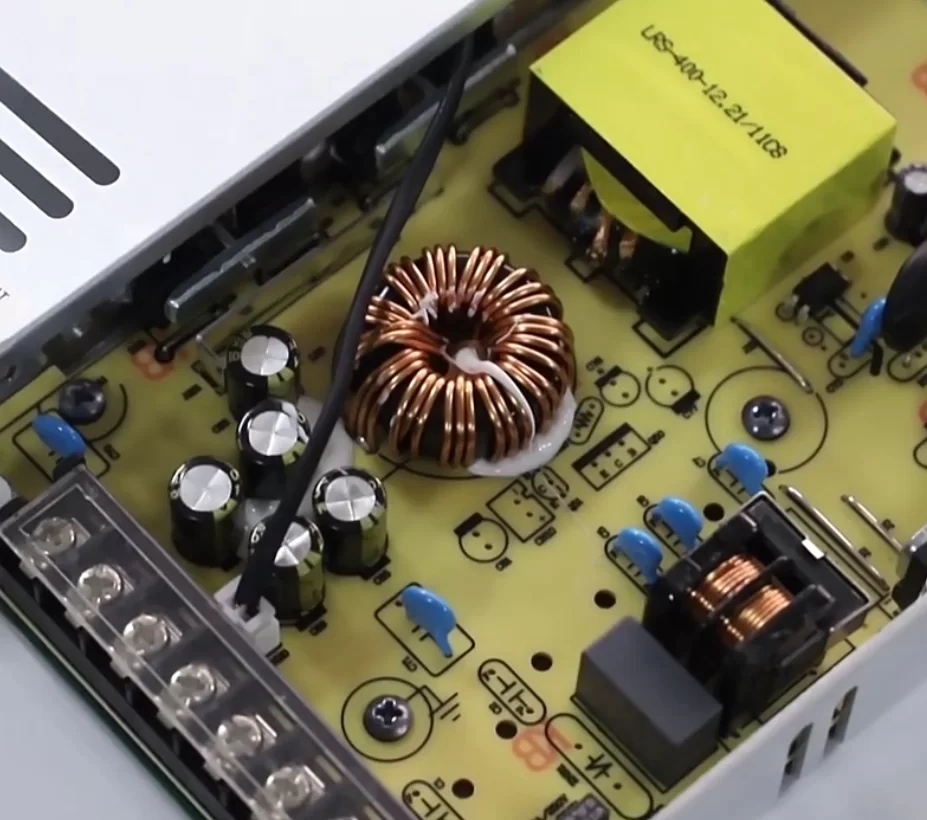

The Interdependence
While distinct, the power supply and the transformer are highly interdependent within many SMPS designs. The transformer’s characteristics significantly influence the overall performance of the power supply. Factors like turns ratio, core material, winding resistance, and leakage inductance all play a crucial role in determining efficiency, regulation, and power handling capabilities.
Conversely, the power supply’s control circuitry dictates the operating conditions of the transformer. The switching frequency, duty cycle, and current waveforms directly impact the transformer’s losses, temperature rise, and saturation characteristics.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the power supply and the transformer are not the same thing. A power supply is a complete system responsible for converting and regulating electrical power, while a transformer is a specific component within that system that performs voltage transformation, isolation, and potentially impedance matching. However, their relationship in SMPS is symbiotic; the transformer is a critical enabler of efficient power conversion, and the power supply’s control circuitry dictates the transformer’s operating environment. A deep understanding of both the system and the component is essential for designing and optimizing high-performance switched-mode power supplies.